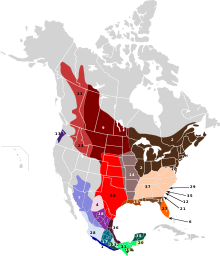
In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in most of Mexico, aside from Lower California, and in southwestern Arizona. It is mostly replaced by the black-tailed or mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) from that point west. However, it is found in mixed deciduous riparian corridors, river valley bottomlands, and lower foothills of the northern Rocky Mountain region from South Dakota west to eastern Washington and eastern Oregon and north to northeastern British Columbia and southern Yukon, including in the Montana Valley and Foothill grasslands.
The conversion of land adjacent to the Canadian Rockies into agriculture use and partial clear-cutting of coniferous trees (resulting in widespread deciduous vegetation) has been favorable to the white-tailed deer and has pushed its distribution to as far north as Yukon. Populations of deer around the Great Lakes have also expanded their range northwards, due to conversion of land to agricultural uses favoring more deciduous vegetation, and local caribou and moose populations. The westernmost population of the species, known as the Columbian white-tailed deer, once was widespread in the mixed forests along the Willamette and Cowlitz River valleys of western Oregon and southwestern Washington, but today its numbers have been considerably reduced, and it is classified as near-threatened. This population is separated from other white-tailed deer populations.
Male white-tailed deer (buck or stag)


Taxonomy
Fawn waving its white tail
Male whitetail in Kansas
Subspecies
O. v. truei, female, Costa Rica
Three O. v. borealis, New Hampshire
Female white-tailed deer (doe)
North America
- O. v. acapulcensis – Acapulco white-tailed deer (southern Mexico)
- O. v. borealis – northern white-tailed deer (the largest and darkest of the white-tailed deer)
- O. v. carminis – Carmen Mountains white-tailed deer (Texas-Mexico border)
- O. v. clavium – Key deer or Florida Keys white-tailed deer (the smallest North American subspecies, found in the lower Florida Keys; an example of insular dwarfism)
- O. v. chiriquensis – Chiriqui white-tailed deer (Panama)
- O. v. couesi – Coues' white-tailed deer, Arizona white-tailed deer, or fantail deer
- O. v. dakotensis – Dakota white-tailed deer or northern plains white-tailed deer (most northerly distribution, rivals the northern white-tailed deer in size)
- O. v. hiltonensis – Hilton Head Island white-tailed deer
- O. v. idahoensis – white-tailed deer (western Canada, Idaho, eastern Washington)[7]
- O. v. leucurus – Columbian white-tailed deer (Oregon and western coastal area)
- O. v. macrourus – Kansas white-tailed deer
- O. v. mcilhennyi – Avery Island white-tailed deer
- O. v. mexicanus – Mexican white-tailed deer (central Mexico)
- O. v. miquihuanensis – Miquihuan white-tailed deer (central Mexico)
- O. v. nelsoni – Chiapas white-tailed deer (southern Mexico and Guatemala)
- O. v. nigribarbis – Blackbeard Island white-tailed deer
- O. v. oaxacensis – Oaxaca white-tailed deer (southern Mexico)
- O. v. ochrourus – northwestern white-tailed deer or northern Rocky Mountains white-tailed deer
- O. v. osceola – Florida coastal white-tailed deer
- O. v. rothschildi – Coiba Island white-tailed deer
- O. v. seminolus – Florida white-tailed deer
- O. v. sinaloae – Sinaloa white-tailed deer(midwestern Mexico)
- O. v. taurinsulae – Bulls Island white-tailed deer (Bulls Island, South Carolina)
- O. v. texanus – Texas white-tailed deer
- O. v. thomasi – Mexican lowland white-tailed deer
- O. v. toltecus – rain forest white-tailed deer (southern Mexico)
- O. v. truei – Central American white-tailed deer (Costa Rica, Nicaragua and adjacent states)
- O. v. venatorius – Hunting Island white-tailed deer (Hunting Island, South Carolina)
- O. v. veraecrucis – northern Veracruz white-tailed deer
- O. v. virginianus – Virginia white-tailed deer or southern white-tailed deer
- O. v. yucatanensis – Yucatán white-tailed deer
South America
- O. v. cariacou – (French Guiana and northern Brazil)
- O. v. curassavicus – (Curaçao)
- O. v. goudotii – (Colombia (Andes) and western Venezuela)
- O. v. gymnotis – South American white-tailed deer (northern half of Venezuela, including Venezuela's Llanos region)
- O. v. margaritae – (Margarita Island)
- O. v. nemoralis – (Central America, round the Gulf of Mexico to Surinam in South America; further restricted from Honduras to Panama)
- O. v. peruvianus – South American white-tailed deer or Andean white-tailed deer (most southerly distribution in Peru and possibly Bolivia)
- O. v. tropicalis – Peru and Ecuador (possibly Colombia)
- O. v. ustus – Ecuador (possibly southern Colombia and northern Peru)
North America
|
Central and South America
|
White-tailed deer buck seen in Missoula, Montana
Description
Female with tail in alarm posture
Size and weight
Close up of female's head
Deer have dichromatic (two-color) vision with blue and yellow primaries;[15] humans normally have trichromatic vision. Thus, deer poorly distinguish the oranges and reds that stand out so well to humans.[16] This makes it very convenient to use deer-hunter orange as a safety color on caps and clothing to avoid accidental shootings during hunting seasons.
Antlers
Male white-tailed deer
White-tailed bucks with antlers still in velvet, August 2011
Ecology
White-tailed deer are generalists and can adapt to a wide variety of habitats.[20] The largest deer occur in the temperate regions of Canada and United States. The northern white-tailed deer (O. v. borealis), Dakota white-tailed deer (O. v. dacotensis), and northwest white-tailed deer (O. v. ochrourus) are some of the largest animals, with large antlers. The smallest deer occur in the Florida Keys and in partially wooded lowlands in the neotropics.Although most often thought of as forest animals depending on relatively small openings and edges, white-tailed deer can equally adapt themselves to life in more open prairie, savanna woodlands, and sage communities as in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. These savanna-adapted deer have relatively large antlers in proportion to their body size and large tails. Also, a noticeable difference exists in size between male and female deer of the savannas. The Texas white-tailed deer (O. v. texanus), of the prairies and oak savannas of Texas and parts of Mexico, are the largest savanna-adapted deer in the Southwest, with impressive antlers that might rival deer found in Canada and the northern United States. Populations of Arizona (O. v. couesi) and Carmen Mountains (O. v. carminis) white-tailed deer inhabit montane mixed oak and pine woodland communities.[21] The Arizona and Carmen Mountains deer are smaller, but may also have impressive antlers, considering their size. The white-tailed deer of the Llanos region of Colombia and Venezuela (O. v. apurensis and O. v. gymnotis) have antler dimensions similar to the Arizona white-tailed deer.
White-tailed deer during late winter
Central American white-tailed deer prefer tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests, seasonal mixed deciduous forests, savanna, and adjacent wetland habitats over dense tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests. South American subspecies of white-tailed deer live in two types of environments. The first type, similar to the Central American deer, consists of savannas, dry deciduous forests, and riparian corridors that cover much of Venezuela and eastern Colombia.[22] The other type is the higher elevation mountain grassland/mixed forest ecozones in the Andes Mountains, from Venezuela to Peru. The Andean white-tailed deer seem to retain gray coats due to the colder weather at high altitudes, whereas the lowland savanna forms retain the reddish brown coats. South American white-tailed deer, like those in Central America, also generally avoid dense moist broadleaf forests.
Since the second half of the 19th century, white-tailed deer have been introduced to Europe.[23] A population in the Brdy area remains stable today.[24] In 1935, white-tailed deer were introduced to Finland. The introduction was successful, and the deer have recently begun spreading through northern Scandinavia and southern Karelia, competing with, and sometimes displacing, native species. The current population of some 30,000 deer originated from four animals provided by Finnish Americans from Minnesota.
Diet
White-tailed deer eat large amounts of food, commonly eating legumes and foraging on other plants, including shoots, leaves, cacti (in deserts), prairie forbs,[25] and grasses. They also eat acorns, fruit, and corn. Their special stomachs allow them to eat some things humans cannot, such as mushrooms and poison ivy. Their diets vary by season according to availability of food sources. They also eat hay, grass, white clover, and other foods they can find in a farm yard. Though almost entirely herbivorous, white-tailed deer have been known to opportunistically feed on nesting songbirds, field mice, and birds trapped in mist nets, if the need arises.[26] A grown deer can eat around 2,000 lb (910 kg) of vegetable matter annually. A foraging area around 20 deer per square mile can start to destroy the forest environment.[27]The white-tailed deer is a ruminant, which means it has a four-chambered stomach. Each chamber has a different and specific function that allows the deer to eat a variety of different foods, digesting it at a later time in a safe area of cover. The stomach hosts a complex set of microbes that change as the deer's diet changes through the seasons. If the microbes necessary for digestion of a particular food (e.g., hay) are absent, it will not be digested.[28]
Predators
Several natural predators of white-tailed deer occur. Wolves, cougars, American alligators, jaguars (in the tropics), and humans are the most effective natural predators of white-tailed deer. These predators frequently pick out easily caught young or infirm deer (which is believed to improve the genetic stock of a population), but can and do take healthy adults of any size. Bobcats, Canada lynx, bears, wolverines, and packs of coyotes usually prey mainly on fawns. Bears may sometimes attack adult deer, while lynxes, coyotes, and wolverines are most likely to take adult deer when the ungulates are weakened by harsh winter weather.[12] Many scavengers rely on deer as carrion, including New World vultures, raptors, foxes, and corvids. Few wild predators can afford to be picky and any will readily consume deer as carrion. Records exist of American crows attempting to prey on white-tailed deer fawns by pecking around their face and eyes, though no accounts of success are given.[29] Occasionally, both golden and bald eagles may capture deer fawns with their talons.[30] In one case, a golden eagle was filmed in Illinois unsuccessfully trying to prey on a large mature white-tailed deer.[31]White-tailed deer typically respond to the presence of potential predators by breathing very heavily (also called blowing) and fleeing. When they blow, the sound alerts other deer in the area. As they run, the flash of their white tails warns other deer. This especially serves to warn fawns when their mother is alarmed.[32] Most natural predators of white-tailed deer hunt by ambush, although canids may engage in an extended chase, hoping to exhaust the prey. Felids typically try to suffocate the deer by biting the throat. Cougars and jaguars will initially knock the deer off balance with their powerful forelegs, whereas the smaller bobcats and lynxes will jump astride the deer to deliver a killing bite. In the case of canids and wolverines, the predators bite at the limbs and flanks, hobbling the deer, until they can reach vital organs and kill it through loss of blood. Bears, which usually target fawns, often simply knock down the prey and then start eating it while it is still alive.[33][34] Alligators snatch deer as they try to drink from or cross bodies of water, grabbing them with their powerful jaws and dragging them into the water to drown.[35]
Most primary natural predators of white-tailed deer have been basically extirpated in eastern North America, with a very small number of reintroduced red wolves, which are nearly extinct, around North Carolina and a small remnant population of Florida panthers, a subspecies of the cougar. Gray wolves, the leading cause of deer mortality where they overlap, co-occur with whitetails in northern Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and parts of Canada.[32] This almost certainly plays a factor in the overpopulation issues with this species.[32] Coyotes, widespread and with a rapidly expanding population, are often the only major nonhuman predator of the species, besides an occasional domestic dog.[32] In some areas, American black bears are also significant predators.[33][34] In northcentral Pennsylvania, black bears were found to be nearly as common predators of fawns as coyotes.[36] Bobcats, still fairly widespread, usually only exploit deer as prey when smaller prey is scarce.[37] Discussions have occurred regarding the possible reintroduction of gray wolves and cougars to sections of the eastern United States, largely because of the apparent controlling effect they have through deer predation on local ecosystems, as has been illustrated in the reintroduction of wolves to Yellowstone National Park and their controlling effect on previously overpopulated elk.[38] However, due to the heavy urban development in much of the East and fear for livestock and human lives, such ideas have ultimately been rejected by local communities and/or by government services and have not been carried through.[39][40][41]
In areas where they are heavily hunted by humans, deer run almost immediately from people and are quite wary even where not heavily hunted. In most areas where hunting may occur deer seem to develop an acute sense of time and a fondness for metro parks and golf courses. This rather odd occurrence is best noted in Michigan, where in the lower peninsula around late August early September they begin to move out of less developed areas in favor of living near human settlements.
The deer of Virginia can run faster than their predators and have been recorded at speeds of 75 km (47 mi) per hour;[42] this ranks them amongst the fastest of all cervids, alongside the Eurasian roe deer. They can also jump 2.7 m (8.9 ft) high and up to 10 m (33 ft) in length. When shot at, the white-tailed deer will run at high speeds with its tail down. If frightened, the deer will hop in a zig-zag with its tail straight up. If the deer feels extremely threatened, however, it may charge the person or predator causing the threat, using its antlers or, if none are present, its head to fight off the threat.
Forest alteration
In certain parts of the eastern United States, high deer densities have caused large reductions in plant biomass, including the density and heights of certain forest wildflowers, tree seedlings, and shrubs. Although they can be seen as a nuisance species, white tail deer also play an important role in biodiversity.[43][44] At the same time, increases in browse-tolerant grasses and sedges and unpalatable ferns have often accompanied intensive deer herbivory.[45] Changes to the structure of forest understories have, in turn, altered the composition and abundance of forest bird communities in some areas.[46] Deer activity has also been shown to increase herbaceous plant diversity, particularly in disturbed areas, by reducing competitively dominant plants;[47] and to increase the growth rates of important canopy trees, perhaps by increased nutrient inputs into the soil.[48]In northeastern hardwood forests, high-density deer populations affect plant succession, particularly following clear-cuts and patch cuts. In succession without deer, annual herbs and woody plants are followed by commercially valuable, shade-tolerant oak and maple. The shade-tolerant trees prevent the invasion of less commercial cherry and American beech, which are stronger nutrient competitors, but not as shade tolerant. Although deer eat shade-tolerant plants and acorns, this is not the only way deer can shift the balance in favor of nutrient competitors. Deer consuming earlier-succession plants allows in enough light for nutrient competitors to invade. Since slow-growing oaks need several decades to develop root systems sufficient to compete with faster-growing species, removal of the canopy prior to that point amplifies the effect of deer on succession. High-density deer populations possibly could browse eastern hemlock seedlings out of existence in northern hardwood forests;[49] however, this scenario seems unlikely, given that deer browsing is not considered the critical factor preventing hemlock re-establishment at large scales.[50]
Ecologists have also expressed concern over the facilitative effect high deer populations have on invasions of exotic plant species. In a study of eastern hemlock forests, browsing by white-tailed deer caused populations of three exotic plants to rise faster than they do in the areas which are absent of deer. Seedlings of the three invading species rose exponentially with deer density, while the most common native species fell exponentially with deer density, because deer were preferentially eating the native species. The effects of deer on the invasive and native plants were magnified in cases of canopy disturbance.[51]
Methods for controlling deer populations
Several methods have been developed in attempts to curb the population of white-tailed deer, and these can be separated into lethal and nonlethal strategies. Most common in the U.S is the use of extended hunting as population control, as well as a way to provide natural meat for humans.[52] In Maryland and many other states, a state agency sets regulations on bag limits and hunting in the area depending on the deer population levels assessed.[53] Hunting seasons may fluctuate in duration, or restrictions may be set to affect how many deer or what type of deer can be hunted in certain regions. For the 2015–2016 white-tailed deer-hunting season, some areas only allow for the hunting of antlerless white-tailed deer. These would include young bucks and females, encouraging the culling of does which would otherwise contribute to increasing populations via offspring production.[52]More refined than public hunting is a method referred to as sharpshooting by the Deer Task Force in the city of Bloomington, Indiana. Sharpshooting can be an option when the area inhabited by the deer is unfit for public hunting. This strategy may work in areas close to human populations, since it is done by professional marksmen, and requires a submitted plan of action to the city with details on the time and location of the event, as well as number of deer to be culled.[54]
Another controversial method involves trapping the deer in a net or other trap, and then administering a chemical euthanizing agent or extermination by firearm. A main issue in questioning the humaneness of this method is the stress that the deer endure while trapped and awaiting extermination.[55]
Nonlethal methods include contraceptive injections, sterilization, and translocation of deer.[56] While lethal methods have municipal support as being the most effective in the short term, some opponents to this view suggest no significant impacts of deer extermination on the populations occur.[57] Opponents of contraceptive methods point out that fertility control cannot provide meat and proves ineffective over time as populations in open-field systems move about. Concerns are voiced that the contraceptives have not been adequately researched for the effect they could have on humans. Fertility control also does nothing to affect the current population and the effects their grazing may be having on the forest plant make-up.[58]
Translocation has been considered overly costly for the little benefit it provides. Deer experience high stress and are at high risk of dying in the process, putting into question its humaneness.[59] Another concern in using this method is the possible spread of chronic wasting disease found in the deer family and the lack of research on its effect on human populations.
Behavior
These bucks were pursuing a pair of does across the Loxahatchee River in Florida—the does lost them by entering a mangrove thicket too dense for the bucks' antlers.
Reproduction
Fawn lying on grass
Females give birth to one to three spotted young, known as fawns, in mid- to late spring, generally in May or June. Fawns lose their spots during the first summer and weigh from 44 to 77 lb (20 to 35 kg) by the first winter. Male fawns tend to be slightly larger and heavier than females. For the first four weeks, fawns are hidden in vegetation by their mothers, who nurse them four to five times a day. This strategy keeps scent levels low to avoid predators. After about a month, the fawns[65] are then able to follow their mothers on foraging trips. They are usually weaned after 8–10 weeks, but cases have been seen where mothers have continued to allow nursing long after the fawns have lost their spots (for several months, or until the end of fall) as seen by rehabilitators and other studies. Males leave their mothers after a year and females leave after two.
Bucks are generally sexually mature at 1.5 years old and begin to breed even in populations stacked with older bucks.
Communication
Two white-tailed deer nuzzling in Cayuga Heights, New York
Marking
White-tailed deer possess many glands that allow them to produce scents, some of which are so potent they can be detected by the human nose. Four major glands are the preorbital, forehead, tarsal, and metatarsal glands. Secretions from the preorbital glands (in front of the eye) were thought to be rubbed on tree branches, but research suggests this is not so. Scent from the forehead or sudoriferous glands (found on the head, between the antlers and eyes) is used to deposit scent on branches that overhang "scrapes" (areas scraped by the deer's front hooves prior to rub-urination). The tarsal glands are found on the upper inside of the hock (middle joint) on each hind leg. Scent is deposited from these glands when deer walk through and rub against vegetation. These scrapes are used by bucks as a sort of "sign-post" by which bucks know which other bucks are in the area, and to let does know a buck is regularly passing through the area—for breeding purposes. The scent from the metatarsal glands, found on the outside of each hind leg, between the ankle and hooves, may be used as an alarm scent. The scent from the interdigital glands, which are located between the hooves of each foot, emit a yellow waxy substance with an offensive odor. Deer can be seen stomping their hooves if they sense danger through sight, sound, or smell; this action leaves an excessive amount of odor for the purpose of warning other deer of possible danger.[67]Throughout the year, deer rub-urinate, a process during which a deer squats while urinating so urine will run down the insides of the deer's legs, over the tarsal glands, and onto the hair covering these glands. Bucks rub-urinate more frequently during the breeding season.[68] Secretions from the tarsal gland mix with the urine and bacteria to produce a strong-smelling odor.[69] During the breeding season, does release hormones and pheromones that tell bucks a doe is in heat and able to breed. Bucks also rub trees and shrubs with their antlers and heads during the breeding season, possibly transferring scent from the forehead glands to the tree, leaving a scent other deer can detect.[70]
Sign-post marking (scrapes and rubs) is a very obvious way white-tailed deer communicate.[70] Although bucks do most of the marking, does visit these locations often. To make a rub, a buck uses his antlers to strip the bark off small-diameter trees, helping to mark his territory and polish his antlers. To mark areas they regularly pass through, bucks make scrapes. Often occurring in patterns known as scrape lines, scrapes are areas where a buck has used his front hooves to expose bare earth. They often rub-urinate into these scrapes, which are often found under twigs that have been marked with scent from the forehead glands.[citation needed]
Human interactions
Three white-tailed deer spotted in Buena Vista, Virginia
At high population densities, farmers can suffer economic damage by deer feeding on cash crops, especially in corn and orchards. It has become nearly impossible to grow some crops in some areas unless very burdensome deer-deterring measures are taken. Deer are excellent fence-jumpers, and their fear of motion and sounds meant to scare them away is soon dulled. Timber harvesting and forest clearance have historically resulted in increased deer population densities,[76][77] which in turn have slowed the rate of reforestation following logging in some areas. High densities of deer can have severe impacts on native plants and animals in parks and natural areas; however, deer browsing can also promote plant and animal diversity in some areas.[78][79] Deer can also cause substantial damage to landscape plants in suburban areas, leading to limited hunting or trapping to relocate or sterilize them. In parts of the Eastern US with high deer populations and fragmented woodlands, deer often wander into suburban and urban habitats that are less than ideal for the species.
Hunting
White-tailed deer have long been hunted as game, for pure sport and for their commodities. Venison, or deer meat, is a very natural and nutritious form of animal protein that can be obtained through responsible and regulated deer hunting. In some areas where their populations are very high, they are considered a pest, and hunting is used as a method to control it.Farming
In New Zealand, America, and Canada, white-tailed deer are kept as livestock, and are extensively as well as intensively farmed for their meat, antlers, and pelts.As pets
Many keep white-tailed deer as pets. They are very smart, affectionate, curious and playful. However, on multiple occasions, during mating season, bucks kept as pets were very aggressive and resulted in severe injuries in their owners. Some areas ban the keeping of white-tailed deer in captivity, while others advocate the trapping and keeping of wild deer as an alternative to hunting due to high populations. However, this is illegal across many U.S. states, as it is considered dangerous; a white-tailed deer's large antlers can impale and kill if that is what the deer intends. Any deer found being held captive will be killed by law enforcement officers in order to prevent the spread of any diseases the deer may have obtained.[80]Many techniques have been investigated to prevent road-side mortality. Fences or road under- or over- passes have been shown to decrease deer-vehicle collisions, but are expensive and difficult to implement on a large scale.[84][85] Roadside habitat modifications could also successfully decrease the number of collisions along roadways.[85] An essential procedure in understanding factors resulting in accidents is to quantify risks, which involves the driver's behavior in terms of safe speed and ability to observe the deer. They suggest reducing speed limits during the winter months when deer density is exceptionally high would likely reduce deer-vehicle collisions, but this may be an impractical solution.[84]
Diseases
Another issue that exists with high deer density is the spreading of infectious diseases. Increased deer populations lead to increased transmission of tick-borne diseases, which pose a threat to human health, to livestock, and to other deer. Deer are the primary host and vector for the adult black-legged tick, which transmits the Lyme disease bacterium to humans.[86] Lyme disease is the most common vector-borne disease in the country and is found in twelve states in Eastern America. In 2009, it affected more than 38,000 people. Furthermore, the incidence of Lyme disease seems to reflect deer density in the eastern United States, which suggests a strong correlation. White-tailed deer also serve as intermediate hosts for many diseases that infect humans through ticks, such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever.[82][83] Newer evidence suggests the white footed mouse is the most significant vector.[87][88]Cultural significance
Odocoileus virginianus skull, part of an exhibition on the cultural artifacts of the Cora people of Western Mexico.



















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.