
The Kamchatka brown bear (Ursus arctos beringianus), also known as the Far Eastern brown bear, or in Russian: Камчатский бурый медведь, romanized: Kamchatsky bury medved, is a subspecies of brown bear.
Description

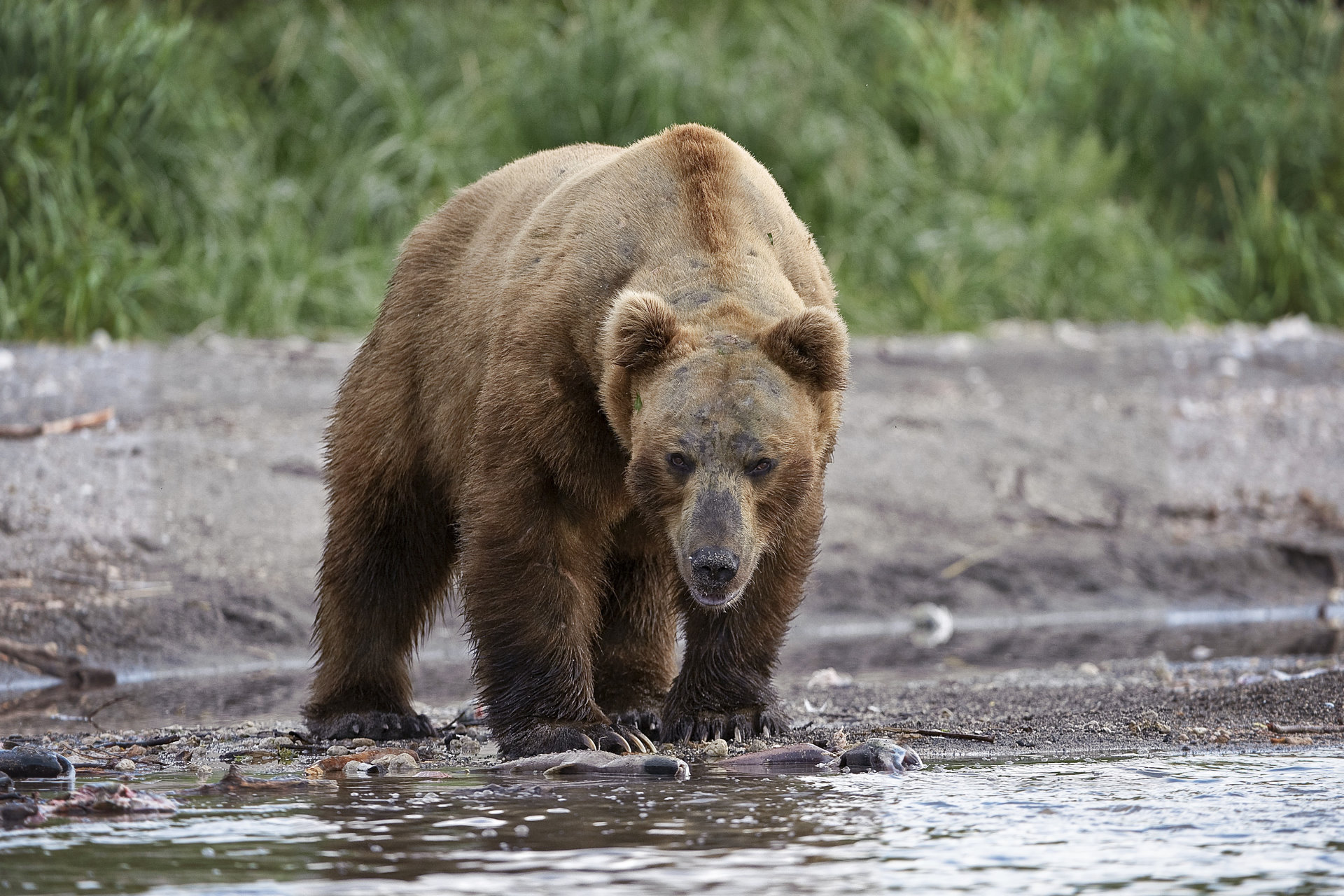
The Kamchatka brown bear is the biggest brown bear in Eurasia,[3] with a body length of 2.4 m (7.9 ft) to 3 m (9.8 ft) tall on hind legs, and a weight up to at least 650 kg (1,430 lb).[4][5] It is about the size of the Kodiak bear; however, the skull is broader than that of the Ussuri brown bear,[6] and compared to that of the Kodiak bear, the breadth of the skull is much greater in proportion to its length, the anterior narial opening is much shorter, and the molars differ in relative size and form.[7] The greatest skull length for males is 40.3–43.6 cm (15.9–17.2 in), and they are 25.8–27.7 cm (10.2–10.9 in) wide, while the skulls of females measure 37.2–38.6 cm (14.6–15.2 in) in length and 21.6–24.2 cm (8.5–9.5 in) in width. Fur colour is predominantly dark brown with a violet tint. Light coloured individuals are rarely encountered.[4]
Distribution

It is native to the Anadyrsky District, the Kamchatka Peninsula, Karaginskiy Island, the Kuril Islands, the coastal strip west of the Sea of Okhotsk southward to the Stanovoy Range, and the Shantar Islands in the Far East. Outside the former Soviet Union, the subspecies occurs in Saint Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea.[4] It is closely related to one clade of brown bears in Alaska and northwest North America, and is thought to be the ancestor of the Kodiak bear.[6]
Behaviour and ecology

In the summer period they feed on blueberries, crowberries, humpback salmon, and steelhead. In autumn, they eat nuts from nut-pines and mountain ash, and fish. In times of famine they eat dead fish or marine mammals, berries, and graminoid vegetation.[4]
Relationship with humans

Kamchatka brown bears are generally not dangerous to humans. During a study on the animal, one researcher found only 1% of his 270 encounters with Kamchatka brown bears resulted in attack.[8] The first Europeans who went to Kamchatka in the 19th century, although surprised by the number and size of bears there, observed that they were relatively harmless, compared to their Siberian counterparts.[9] However, in July 2008, a platinum-mining compound in the Olyutorsky District of Kamchatka Krai was besieged by a group of 30 starving bears who killed two guards.[10]
Trophy hunting
Kamchatka brown bears are among the most prized trophies for the Russian hunting industry. In 2005 the Kamchatka Department of Wildlife Management issued 500 hunting permits. Clients paid up to $10,000 to hunt bears. Thus, the economic impacts from recreational hunting of Kamchatka brown bears are significant. The recreational hunting of Kamchatka Brown Bears has led to endangerment of the species in Russia[3]
_1571040380_1603697943.jpg)
Ursus arctos beringianus
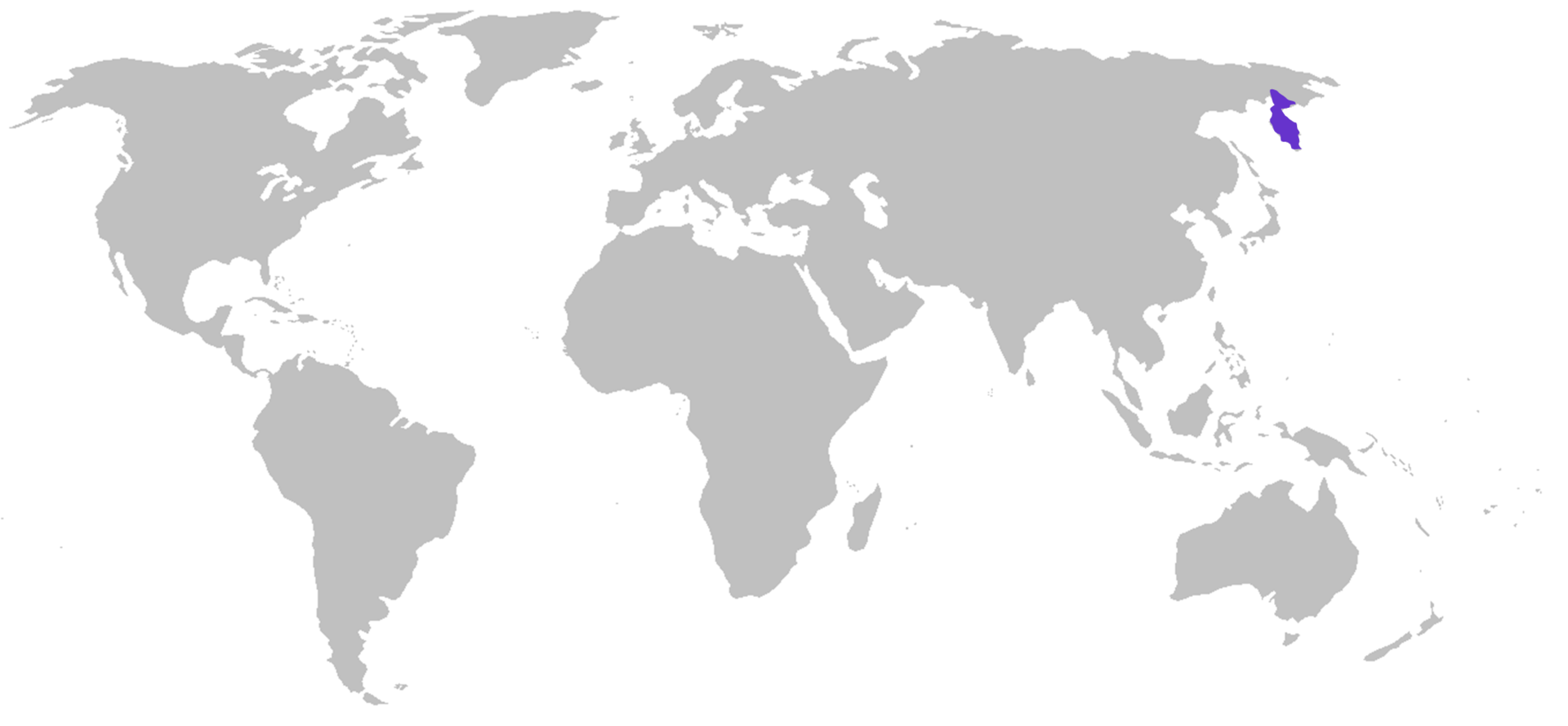
Ursus arctos beringianus range map.








No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.