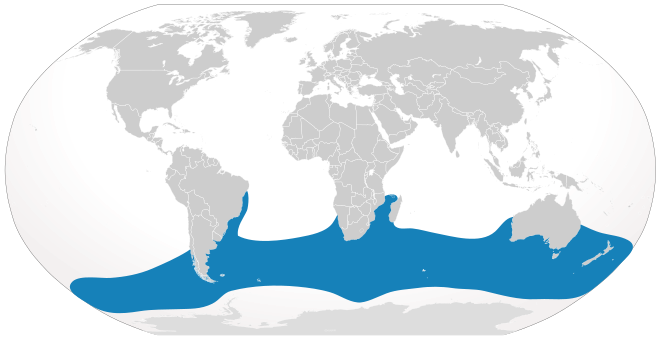
Approximately 10,000 southern right whales are spread throughout the southern part of the Southern Hemisphere.

Taxonomy
Right whales were first classified in the genus Balaena in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus, who at the time considered all right whales (including the bowhead) to be a single species. Through the 1800s and 1900s, in fact, the family Balaenidae has been the subject of great taxonometric debate. Authorities have repeatedly recategorized the three populations of right whale plus the bowhead whale, as one, two, three or four species, either in a single genus or in two separate genera. In the early whaling days, they were all thought to be a single species, Balaena mysticetus.[4]The southern right whale was initially described as Balaena australis by Desmoulins in 1822. Eventually, it was recognized that bowheads and right whales were in fact different, and John Edward Gray proposed the genus Eubalaena for the right whale in 1864. Later, morphological factors such as differences in the skull shape of northern and southern right whales indicated at least two species of right whale—one in the Northern Hemisphere, the other in the Southern Ocean.[4] As recently as 1998, Rice, in his comprehensive and otherwise authoritative classification, Marine mammals of the world: systematics and distribution, listed just two species: Balaena glacialis (all of the right whales) and Balaena mysticetus (the bowheads).[5]
In 2000, Rosenbaum et al. disagreed, based on data from their genetic study of DNA samples from each of the whale populations. Genetic evidence now clearly demonstrates that the northern and southern populations of right whale have not interbred for between 3 million and 12 million years, confirming the southern right whale as a distinct species. The northern Pacific and Atlantic populations are also distinct, with the North Pacific right whale being more closely related to the southern right whale than to the North Atlantic right whale.[6] Genetic differences between E. japonica (north pacific) and E. australis (south pacific) are much smaller than other baleen whales represent among different ocean basins.[7]
It is believed that the right whale populations first split because of the joining of North and South America. The rising temperatures at the equator then created a second split, into the northern and southern groups, preventing them from interbreeding.[8]
In 2002, the Scientific Committee of the International Whaling Commission (IWC) accepted Rosenbaum's findings, and recommended that the Eubalaena nomenclature be retained for this genus.[9]
The cladogram is a tool for visualizing and comparing the evolutionary relationships between taxa. The point where a node branches off is analogous to an evolutionary branching – the diagram can be read left-to-right, much like a timeline. The following cladogram of the family Balaenidae serves to illustrate the current scientific consensus as to the relationships between the southern right whale and the other members of its family.
| Family Balaenidae | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| The right whale family, Balaenidae[6] |
Description
Two distinctive coloration patterns.
An adult female is 15 m (49 ft)[12] and can weigh up to 47 tonnes (46 long tons; 52 short tons),[12] with the larger records of 17.5–18 m (57–59 ft)[13][14] in length and 80 tonnes (79 long tons; 88 short tons)[15] or up to 90 tonnes (89 long tons; 99 short tons) in weight,[16] making them slightly smaller than other right whales in the Northern Hemisphere.[17] The testicles of right whales are likely to be the largest of any animal, each weighing around 500 kg (1,100 lb). This suggests that sperm competition is important in the mating process.[18]
Right whales do not normally cross the warm equatorial waters to connect with the other species and (inter)breed: their thick layers of insulating blubber make it difficult for them to dissipate their internal body heat in tropical waters. However, based on historical records and unconfirmed sightings in modern periods, E. australis transits may indeed occur through equatorial waters.[19] Moreover, a stranding of "a 21.3 m (71 feet) long right whale at Gajana, northwestern India in November, 1944" was reported, however, true identity of this animal is unclear.[20][21]
The proportion and numbers of molten-coloured individuals are notable in this species compared with the other species in the Northern Hemisphere. Some whales remain white even after growing up.[22]
Life span is not clear although whales seem to reach over 100 years old.[23]
Behavior
"Sailing"
They have very strong maternal connections with locations and gene pools they were born in,[27][28] and especially males may follow patterned migration routes.[29] Calving females are known to return to their 'birth spots' at 3-years intervals[30] as the most commonly seen calving intervals are 3 years which may vary from 2 up to 21 years due to multiple factors.[31][32] Specific congregation areas in the same region may function as for different objectives for whales.[33]
This species has been recognized to nurse unrelated orphans on occasions.[34]
Population and distribution
The southern right whale spends summer in the far Southern Ocean feeding, probably close to Antarctica. If the opportunity arises, feeding can occur even in temperate waters such as along Buenos Aires.[35][36] It migrates north in winter for breeding and can be seen by the coasts of Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Namibia, Mozambique, Peru, Tristan de Cunha, Uruguay, Madagascar, New Zealand and South Africa, however, whales have been known to winter on sub-Antarctic regions.[37][38] The total population is estimated to be around 10,000. Since hunting ceased, stocks are estimated to have grown by 7% a year. It appears that the South American, South African and Australasian groups intermix very little if at all, because maternal fidelity to feeding and calving habitats is very strong. The mother also passes these choices to her calves.[39]Whaling records among the hemisphere including a certain whaling ground in central northern Indian Ocean[40] and recent sightings among near-equatorial regions have occurred, and if the later mentioned sighting off Kiribati was truly of E. australis, this species could cross the Equator on irregular occasions and their original distributions might have been much broader and more northerly distributed than that of the present status.[19][41] As above mentioned, there was one record of a "right whale" stranded at northwestern coast of continental India.
Other than sheltered and calm waters, calving grounds have been identified close to high wave coastal areas, vicinity to land cliffs and deep waters where sounds of waves may prevent predators' acoustics searches for infants and calving cows, and deep areas close to shallows may function as training grounds for calves to prepare for upcoming migrations to feeding grounds.[42]
The most recent population estimates, published by National Geographic in October 2008, put the southern whale population at 10,000. An estimate of 7,000 followed a March 1998 IWC workshop. Researchers used data about adult female populations from three surveys (one in each of Argentina, South Africa and Australia, collected during the 1990s) and extrapolated to include unsurveyed areas, number of males and calves using available male:female and adult:calf ratios to give an estimated 1999 figure of 7,500 animals.[43] Recovery of the overall population size of the species is predicted to be at less than 50% of its pre-whaling state by 2100 due to heavier impacts of whaling and slower recovery rates.[44]
Aside from impacts on whales and environments caused by mankind, their distributions and residences could be largely effected by presences of natural predators or enemies,[37] and similar trends are also expectable for other subspecies.[45]
Many locations throughout the Southern Hemisphere were named after current or former presences of southern rights, including Walvis Bay, Punta Ballena, Right Whale Bay, Otago Harbour, Whangarei Harbour, Foveaux Strait,[46] South Taranaki Bight, Moutohora Island and Wineglass Bay.
Africa
Breaching in the De Hoop Nature Reserve
A mating group in Hermanus Bay: one female and two males
South Africa
Hermanus in South Africa has become known as a mecca for whale watching, during the Southern Hemisphere winter months (June – October) the southern right whales migrate to the coastal waters of South Africa, with in excess of 100 whales known to be in the Hermanus area. Whilst in the area, the whales can be seen with their young as they come to Walker Bay to calve and mate. Many behaviours such as breaching, sailing, lobtailing, or spyhopping can be witnessed. In False Bay whales can be seen from the shore from July to October while both Plettenberg Bay and Algoa Bay are also home to the southern right whales from July to December. They can be viewed from land as well as by boat with licensed operators conducting ocean safaris throughout the year.Recent increases in numbers of whales visiting the north-eastern part of South Africa, the so-called Dolphin Coast such as around Ballito[47] and off Umdloti Beach,[48] indicates the whales' normal ranges are expanding and that re-colonising historical habitats will likely continue as more whales migrate further north.
Western Africa
In Namibia, the majority of confirmed whales are restricted to the south of Luderitz, the southern edge of the country, and only a handful of animals, but with good increases in numbers, venture further north to historical breeding grounds such as at Walvis Bay. Until hunting, including illegal mass operations by Soviet Union ceased, whales had been rare along Namibian shores as no sighting records north of Orange River until 1971,[49] and the first calving activities were confirmed as late as the 1980s.[50]Historical records suggest that this whale's regular range could have reached further north up the coasts of Cape Fria (northern Namibia)[51] and Angola as far as Baia dos Tigres (Tiger Bay).[52][51]
Whaling was taken place in Gabon[19] such as at Cape Lopez, and there have been a few of unconfirmed sightings in recent years including one by Jim Darling, a renowned whale researcher.[53][54]
Eastern Africa
Rare appearance along Madagascar at Île Sainte-Marie
Mid–South Atlantic
Due to illegal whaling by the Soviet Union, the recovery of many stocks including the population off Tristan da Cunha[69] and adjacent areas such as Gough Island had been severely hindered, resulting in relatively few numbers of visiting animals.Based on capture records, whales once reached to the island of Saint Helena as well.[41]
Latin America
Brazil
Cow – calf pair at Abrolhos
Whaling records including those prior to by Maury and Townsend indicate that whales, at least more commonly ventured or migrated to further north than today such as at Salvador, Bahia.[19][41]
Argentina
Submerges off Valdes Peninsula
Uruguay
In Uruguay, coastal areas such as Punta del Este host congregating sites for whales in breeding seasons, but not likely as calving grounds.[105] Their recovery helped create a whale-sanctuary off Latin America;[106] the creation of this protected area had been prevented for nearly a decade by pro-whaling nations such as Japan.Chile and Peru
For the critically endangered Chile/Peru population, the Cetacean Conservation Center (CCC) has been working on a separate program for right whales. This population, containing no more than 50 or less individuals, is under threats of increasing ship lanes and fishing industries.[107] 124 sightings in total had been recorded during 1964–2008 period.[108] Aside from vagrants' records, Peru's coastlines possibly host one of the northernmost confirmed range of the species along with Gabon,[19] Senegal, Tanzania, Brazilian coasts, Madagascar, Indian Ocean, western Australia, Kermadec Islands, and tropical waters including South Pacific Islands.[19] The Alfaguara project targeting cetaceans in Chiloe[109][110] may possibly target this species as well in the future since calving activities have been confirmed in Chiloé Archipelago.[111] Foraging grounds of this population is currently undetected, but possibly Chiloé and down south of Caleta Zorra to southern fiords such as from Penas Gulf to Beagle Channel although numbers of confirmations are small in the Beagle Channel. .[112] Some hopes arising for establishment of new tourism industry in eastern side of the Strait of Magellan[113] most notably in the vicinity of Cape Virgenes[114] and Punta Dungeness as the number of sightings increases.[115][116][117] It is unknown whether these increases are due to re-colonisation by whales from the Patagonian population.Occurrences of brindle individuals have been confirmed from this population as well.[118][119]
Oceania
Historically, populations in Oceanian regions had been very robust.[41] There were stories of early settlers complaining that sounds of cavorting whales kept them awake at night in various locations such as on Wellington Bay and River Derwent. Satellite tracking conducted suggests that there are at least some interactions between populations in these two nations,[120][121] but the extent thereof is unknown. Furthermore, historical distributions of New Zealand and southeast or east Australian groups have been speculated to share at least calving grounds, and significant losses of local calving grounds may provide habitats to different groups.[122]Australia
Southern right whales in Australian waters show higher rate of recoveries, as they have increased from 2,100 whales in 2008[123] to 3,500 individuals in 2010.[30] Two genetically distinct groups inhabit Australian waters: the southwestern population of 2,900 whales - in 2012 currently holding the majority of the overall Australian population - and the critically endangered southeastern group, counting only dozens to 300 individuals.Right whales can be found in many parts of southern Australia, where the largest population is found at the Head of the Bight in South Australia, a sparsely populated area south of the middle of the Nullarbor Plain. Over 100[124] individuals are seen there annually from June to October. Visitors can view the whales from cliff-top boardwalks and lookouts, with whales swimming almost directly below. A more accessible South Australian location for viewing whales is Encounter Bay where the whales can be seen just off the beaches of the Fleurieu Peninsula, centred around the surfing town of Middleton. The whales have established a newer nursery-ground near Eyre Peninsula, especially at Fowlers Bay. Numbers are much smaller at these locations compared to those in the Bight, with an average of a couple of whales per day, but as of 2009 there were regular sightings of more than ten whales at a time off Basham Beach, near Middleton.[125] The South Australian Whale Centre at Victor Harbor has information on the history of whaling and whale-watching in the area, and maintains an on-line database of whale sightings.[126] Whale numbers are scarcer in Victoria, where the only established breeding ground which whales use each year, in very small numbers, is at Warrnambool. However, as the whales do seem to be increasing in number generally, but not showing any dramatic increases at Warrnambool, they may be extending their wintering habitats into other areas of Victoria, where the numbers of sightings are slowly increasing. These areas include around Melbourne, such as in Port Phillip Bay, along Waratah Bay, at Ocean Grove, Warrnambool, on Mornington Peninsula, in Apollo Bay, and on Gippsland coasts and at Wilsons Promontory. Tasmania is another, newer, wintering ground showing dramatic increases in recent years. The waters off the Western Australia, New South Wales, and Queensland coasts had previously been inhabited by whales. Their historical range was much wider and was spread around the southern coast of the continent, extending up to Australian Abrolhos Island,[127] Exmouth and Shark Bay on the west coast, and to Hervey Bay and Moreton Bay to Great Barrier Reef[128] or further north on the east coast. The east-coast population remains endangered and very small (in the low-tens),[129] contributing in small numbers and limited re-colonization, but increases have been confirmed in many areas such as the vicinity of Port Jackson, Port Stephens, Twofold Bay, Jervis Bay, Broulee,[130] Moruya River,[131][132] Narooma,[133] Byron Bay,[134] and so on, and there have been 12 foraging areas officially announced[by whom?].[135]
Whale numbers visiting historical habitats of sub-Antarctic regions show drastic differences in quantity for respective locations: recovering well at the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands while less successful at Macquarie Island.[136]
It is not known whether Australian populations will re-colonise historical oceanic habitats such as Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island with Lord Howe Seamount Chain (historically known as the "Middle Ground" for whalers[137][need quotation to verify][138]) in the future.
New Zealand
Many features are still unknown about current right whale population(s) in New Zealand waters. However, studies by the Department of Conservation and sightings reported by locals helped to deepen understanding.[139] Pre-exploitation size of New Zealand group could have been up from 28,800 to 47,100 in total where 35,000 to 41,000 catches were made between 1827 and 1980. The number of whales survived commercial and illegal whaling operations might be decreased to as few as 30 whales.[122][140] Not a single sighting or stranding was recorded between 1928 and 1963 on main islands, and full recovery is estimated to take about 60 years. As below mentioned, if illegal mass operations by Soviet with supports from Japan taken 372 whales in 1960s[141] had not been taken place, New Zealand population could have been three or four times larger than the current size.[142] Furthermore, considerably small genetic diversity of this population, caused by whaling operations, has been concerned and which is even lower than that of more endangered North Atlantic right whales.[143]The population at the sub-Antarctic Auckland Islands is showing a remarkable recovery but with the lowest genetic diversities in the world,[143] while the recovery state in Campbell Islands is slower,[38] and possible number of whales after the World War 2 could have been fewer than 20 individuals in total.[120] Right whales had not been confirmed on main islands for 36 years until 1963 when 4 separate sightings including a cow-calf pair were made among wide range, and remnants of sub-Antarctic populations were re-discovered in 1990s as opportunistic sightings had been reported in 1980s.[120]
Today, the majority of right whales congregate at Auckland and Campbell Islands and forming exceptionally dense and limited congregations including all the sex groups such as mating adults and calving females within and adjacent to Port Ross,[144] where up to 200 whales may winter at the same time.[145] It is notable that whales, including all the age groups[146] are present in this small area annually, not only as feeding and summering[147] grounds but also mainly for wintering, breeding, and calving during harsh, cold periods. Low genetic diversities due to whaling pressures caused changes in skin colorations on this group as well.[143] Scientists used to believe there was a very small remnant population of southern right whales inhabiting New Zealand's main islands (North and South Island), containing probably 11 reproductive females.[148] In winter, whales migrate north to New Zealand waters and large concentrations occasionally visit the southern coasts of South Island. Bay areas along Foveaux Strait from Fiordland region to northern Otago are important breeding habitats for right whales, especially Preservation[149] and Chalky Inlets,[150] Te Waewae Bay,[151] and Otago Peninsula.[152][153] Calving activities are observed all around the nation, but with more regularity around North Island shores from the Taranaki coast in the west to Hawke's Bay, Bay of Plenty in the east, and areas in Hauraki Gulf such as Firth of Thames or Bay of Islands in the north.
There are various parts of the nation where large numbers of whales were seen historically, but sightings are less common nowadays. These areas include the Marlborough Region, especially from Clifford Bay and Cloudy Bay to Port Underwood,[154] Golden Bay, Awaroa Bay, and coastlines on West Coast and Hokianga Harbour in Northland. Other than a handful of confirmed observations, very little information is available for modern migrations to historical oceanic habitats of Kermadec Islands[155][156] and Chatham Islands.[157] Northernmost of historic records was at 27°S.[158]
Recent study revealed that the right whale populations from New Zealand's main islands and the sub-Antarctic islands interbreed, though it is still unknown whether the two stock originally came from a single population.[159] Feeding areas in pelagic waters are rather unclear while congregations have been confirmed along southern edge of the Chatham Rise.[160]
It is unclear whether (part of) whales found either historically or currently on areas within Australian ranges that are located close to the ranges of New Zealand whales such as Norfolk Island and Macquarie Island, do or do not originate in New Zealand group(s).
Other
It is unclear whether right whales have historically or currently distributed among parts of hemisphere lacking great land masses and reached far more pelagic islands such as Alejandro Selkirk and Robinson Crusoe Islands, Hanga Roa, Pitcairn, Galapagos Islands, and the Easter Island.
Populations among sub-Antarctic islands in the Scotia Sea[71] such as South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands and Falkland Islands were severely damaged and showing slower recoveries. Antarctic distributions are also rather unclear due to low levels of sightings around oceanic islands in these areas, such as at Elephant Island.[162]
Indian Ocean
Historical populations which summered in Crozet Islands and Kerguelen Islands, and migrated to La Roche Godon and Île Saint-Paul, Île Amsterdam, and Central Indian Ocean once existed, and which might be distinct from whales seen on Mozambique coasts.[163] Repopulating among these areas in Indian Ocean is likely to be even at slower recovery-rates than other areas as occurrences of sightings have been fewer in modern periods among Crozet,[164][165] Réunion,[166][56][167][168] Mauritius, Marion Islands,[37] Île Amsterdam, and Kerguelen.[169]Catches had occurred on central Indian Ocean near the Equator, especially around the area between Diego Garcia, Egmont Islands, and Great Chagos Bank in west, and Cocos (Keeling) Islands in east, being comparable to the range of some other stocks among Latin America, Africa, and south Pacific islands including Kiribati, the northernmost occurrences of all the populations known today.[40]
Whaling
Sculpture of southern right whale at Cockle Creek on Recherche Bay, Tasmania, where bay whaling was performed extensively during the 1840s and 1850s
The southern right whale had been coming to New Zealand waters in large numbers before the 19th century, but was extensively hunted from 1830–1850. Hunting gradually declined with the whale population and then all but ended in coastal New Zealand waters.[170] The beginning of the 20th century brought industrial whaling, and the catch grew rapidly. By 1937, according to whalers' records, 38,000 were captured in the South Atlantic, 39,000 in the South Pacific, and 1,300 in the Indian Ocean. Given the incompleteness of these records, the total take was somewhat higher.[171]
As it became clear that stocks were nearly depleted, right whaling was banned in 1937. The ban was largely successful, although some illegal whaling continued for several decades. Madeira took its last two right whales in 1968. Illegal whaling continued off the coast of Brazil for many years and the Imbituba station processed right whales until 1973. The Soviet Union admitted illegally taking over 3,300 during the 1950s and 1960s,[172] although it only reported taking 4.[173] Illegal operations continued even in 70s, such as the case in Brazil until 1973.[13] It was also revealed that Japan was supporting these destructive hunts by neglecting and disregarding monitoring obligations. Furthermore, there were agreements between Japan and the Soviet Union to keep their illegal mass whaling activities in foreign/international protected waters in confidence.[174]
Whales began to be seen again in Australian and New Zealand waters from the early 1960s.[170] It is claimed that if the illegal hunts by the Soviet Union had never happened, the New Zealand population would be three or four times larger than its current size.[142]
Conservation
The southern right whale, listed as "endangered" by CITES, is protected by all countries with known breeding populations (Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, New Zealand, South Africa and Uruguay). In Brazil, a federal Environmental Protection Area encompassing some 1,560 km2 (600 sq mi) and 130 km (81 mi) of coastline in Santa Catarina State was established in 2000 to protect the species' main breeding grounds in Brazil and promote regulated whale watching.[175] The southern right whale is listed on Appendix I[176] of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS) as this species has been categorized as being in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant proportion of their range. This species is also covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MoU).[177]A two-year, £740,000 project, led by the British Antarctic Survey began in 2016, to discover why almost 500 young have been washed up on the Valdes Peninsula over the last ten years. The project is funded by the UK's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) and the EU. Possible reasons are a lack of krill in the whale feeding grounds at South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, exposure to toxic algae and attacks by kelp gulls (Larus dominicanus).[178]
Whale and gull off Península Valdés
Gull attacks
One possibly significant contributor to the calf mortality rate has alarmed scientists – since at least 1996, kelp gulls off the coast of Patagonia have been observed attacking and feeding on live right whales.[179] The kelp gull uses its powerful beak to peck down several centimetres into the skin and blubber, often leaving the whales with large open sores – some of which have been observed to be half a meter in diameter. This predatory behavior, primarily targeted towards mother/calf pairs, has been continually documented in Argentinian waters, and continues today. Observers note that the whales are spending up to a third of their time and energy performing evasive maneuvers – therefore, mothers spend less time nursing, and the calves are thinner and weaker as a result. Researchers speculate that many years ago, waste from fish processing plants allowed the gull populations to soar. Their resulting overpopulation, combined with reduced waste output, caused the gulls to seek out this alternative food source.[180] Scientists fear that the gulls' learned behaviour could proliferate, and the IWC Scientific Committee has urged Brazil to consider taking immediate action if and when similar gull behaviour is observed in their waters. Such action may include the removal of attacking gulls, following Argentina's lead in attempting to reverse the trend.[94]Whale watching
Africa
Whale breaching off George, Western Cape with a tanker behind.
Whales are occasionally observed during tours in Namibia, Mozambique and Madagascar, where sighting rates along Namibian coasts shows dramatic increases in the recent years.
Latin America
Though their numbers are dangerously small, land-based sightings of whales are on the increase in recent years off Chile and Peru, with some hope of creating new tourism industries,[194] especially in the Strait of Magellan, most notably around Cape Virgenes.[116]
Oceania
Whales cavort next to surfers on Manly Beach.
Similarly, southern right whales may provide chances for the public to observe whales from shore on New Zealand's coasts with greater regularity than in the past, especially in southern Fiordland, Southland through to the Otago coast,[195] and on the North Island coast, especially in Northland and other locations such as the Bay of Plenty and the South Taranaki Bight. Births of calves could have always been occurring on the main islands' coasts, but were confirmed with two cow-calf pairs in 2012.[196][197]
Subantarctic
In the Subantarctic Islands and in the vicinity of Antarctica,[198] where few regulations exist or are enforced, whales can be observed on expedition tours with increasing probability. The Auckland Islands are a specially designated sanctuary for right whales, where whale-watching tourism is prohibited without authorization.[199]















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.