The kea nests in burrows or crevices among the roots of trees. Kea are known for their intelligence and curiosity, both vital to their survival in a harsh mountain environment. Kea can solve logical puzzles, such as pushing and pulling things in a certain order to get to food, and will work together to achieve a certain objective.[6] They have been filmed preparing and using tools.[7]
Taxonomy and naming
The kea was described by ornithologist John Gould in 1856.[8] Its specific epithet, the Latin term notabilis, means "noteworthy".[9] The common name kea is from Māori, probably an onomatopoeic representation of their in-flight call – ‘keee aaa’.[10] The word "kea" is both singular and plural.The genus Nestor contains four species: the New Zealand kaka (Nestor meridionalis), the kea (N. notabilis), the extinct Norfolk kaka (N. productus), and the extinct Chatham kaka (N. chathamensis). All four are thought to stem from a "proto-kākā", dwelling in the forests of New Zealand five million years ago.[11][12] Their closest relative is the flightless kakapo (Strigops habroptilus).[11][12][13][14] Together, they form the parrot superfamily Strigopoidea, an ancient group that split off from all other Psittacidae before their radiation.[11][12][14][15]
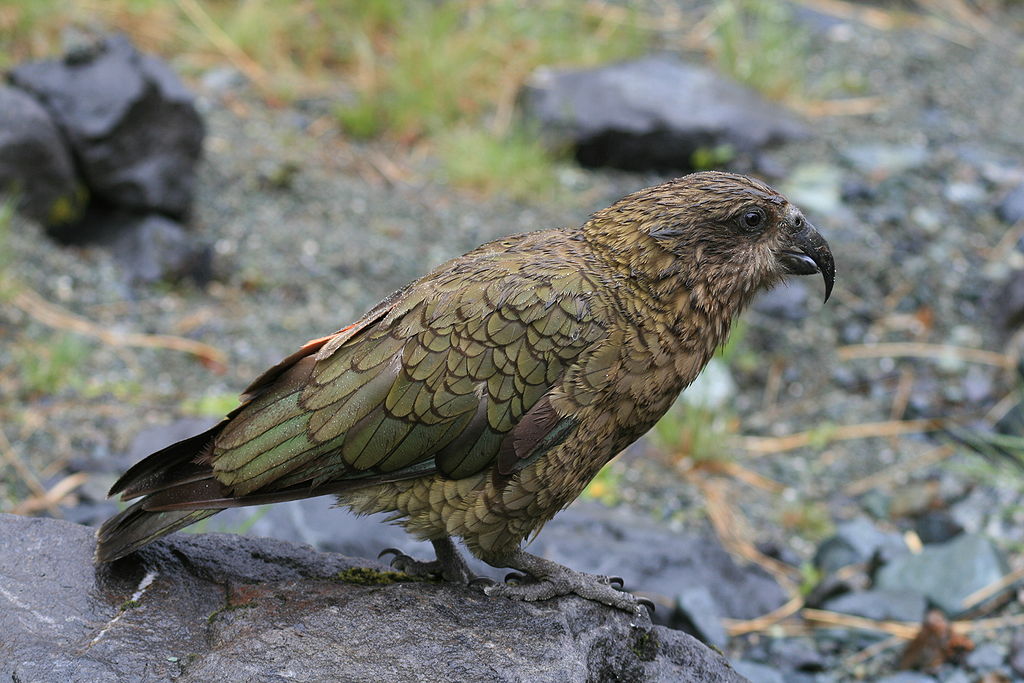
Description
Kea in flight
Orange feathers can be seen under the wing during flight
Juveniles have yellow eyerings and cere, an orange-yellow lower beak, and grey-yellow legs
Distribution and habitat
The kea ranges from lowland river valleys and coastal forests of the South Island's west coast up to the alpine regions of the South Island such as Arthur's Pass and Aoraki / Mount Cook National Park, closely associated throughout its range with the southern beech (Nothofagus) forests in the alpine ridge. Apart from occasional vagrants, kea are not found in the North Island, although fossil evidence suggests a population lived there over 10,000 years ago.[19][20]
The population was estimated at between 1,000 and 5,000 individuals in 1986,[21] contrasting with another estimate of 15,000 birds in 1992.[22] The kea's widespread distribution at low density across inaccessible areas prevents accurate estimates.[23][24]
Current population estimates suggest that between 3000 and 7000 individuals are left.[25]
Kea investigating tourists
Behaviour
Breeding
Kea chick, Weltvogelpark Walsrode, Germany
Kea are social and live in groups of up to 13 birds.[27] Isolated individuals do badly in captivity, but respond well to mirror images.[28]
In one study, nest sites occur at a density of one per 4.4 square kilometres (1.7 sq mi).[29] The breeding areas are most commonly in southern beech (Nothofagus) forests, located on steep mountainsides. Breeding at heights of 1,600 metres (5,200 ft) above sea level and higher, it is one of the few parrot species in the world to regularly spend time above the tree line. Nest sites are usually positioned on the ground underneath large beech trees, in rock crevices, or dug burrows between roots. They are accessed by tunnels leading back 1 to 6 metres (3.3 to 19.7 ft) into a larger chamber, which is furnished with lichens, moss, ferns, and rotting wood. The laying period starts in July and reaches into January.[30] Two to five white eggs are laid, with an incubation time of around 21 days, and a brooding period of 94 days.[31]
Mortality is high among young kea, with less than 40% surviving their first year.[32] The median lifespan of a wild subadult kea has been estimated at five years, based on the proportion of kea seen again in successive seasons in Arthur's Pass, and allowing for some emigration to surrounding areas. Around 10% of the local kea population were expected to be over 20 years of age.[22] The oldest known captive kea was 50 years old in 2008.[32]
Diet and feeding
An omnivore, the kea feeds on more than 40 plant species, beetle larvae, other birds (including shearwater chicks), and mammals (including sheep and rabbits).[6][27] It has been observed breaking open shearwater nests to feed on the chicks after hearing the chicks in their nests.[33] The kea has also taken advantage of human garbage and "gifts" of food.[34]Sheep
Sheep, suspected to have been killed by kea in July 1907
Since Kea are now a protected species, their depredations are generally tolerated by sheep farmers, though why some Kea attack sheep, and others do not, remains unclear. Various theories, including similarities with existing food sources, curiosity, entertainment, hunger, maggots as well as a progression from scavenging dead sheep and hides have all been put forward as to how the behaviour was first acquired.[37][39] Anecdotal evidence also suggests only particular birds have learned the behaviour, with identification and removal of those individuals being sufficient to control the problem.[39][20]
There are also anecdotal reports of kea attacking rabbits, dogs, and even horses.[37] There are also suggestions that Kea used to feed on Moa in a similar way.[39]
Relationship with humans
Kea damaging a parked car
Adult Kea close-up at Milford Sound, New Zealand
People commonly encounter wild kea at South Island ski areas, where they are attracted by the prospect of food scraps. Their curiosity leads them to peck and carry away unguarded items of clothing, or to pry apart rubber parts of cars — to the entertainment and annoyance of human observers. They are often described as "cheeky". A kea has even been reported to have made off with a tourist's passport while he was visiting Fiordland National Park.[41]
The Department of Conservation also suggest that the time savings resulting from a more calorie-rich diet will give kea more free time to investigate and hence damage things at campsites and car parks.[42]
The birds' naturally trusting behaviour around humans has also been indicated as a contributing factor in a number of recent incidents at popular tourist spots where kea have been purposely killed.[43][44][45]
Kea were eaten by Māori. They were believed by the Waitaha tribe to be kaitiaki (guardians).[46]
Cultural references
The kea featured on the reverse side of the New Zealand $10 note between 1967 and 1992, when it was replaced with the whio.Kea are the protagonists in New Zealand author Philip Temple's novels Beak of the Moon (1981) and Dark of the Moon (1993), recounting respectively the first encounters of a group of kea with humans at the time of the colonisation of the South Island by Māori, and their life in present-day, human-dominated New Zealand.
The youngest section of Scouts New Zealand (known as Beavers in the United Kingdom and Joeys in Australia) is named after the bird.
In the video game Dwarf Fortress, kea are one of many species of animals that will steal the player's items.[47]
A gathering or group of kea is called a circus.[48]
Threats
Together with local councils and runholders, the New Zealand government paid a bounty for kea bills because the bird preyed upon livestock, mainly sheep.[37][49][20] It was intended that hunters would kill kea only on the farms and council areas that paid the bounty, but some hunted them in national parks and in Westland, where they were officially protected. More than 150,000 were killed in the hundred years before 1970, when the bounty was lifted.[50]A study of kea numbers in Nelson Lakes National Park showed a substantial decline in the population between 1999 and 2009, caused primarily by predation of kea eggs and chicks.[51] Video cameras set up to monitor kea nests in South Westland showed that possums killed kea fledglings.[52]
Lead poisoning, mostly from the roofs of buildings/building materials, is also a significant cause of premature deaths among kea.[53][54] Research on lead toxicity in kea living at Aoraki / Mount Cook found that of 38 live kea tested all were found to have detectable blood lead levels, 26 considered dangerously high.[54] Additional analysis of 15 dead kea sent to Massey University for diagnostic pathology between 1991 and 1997 found 9 bodies to have lead blood levels consistent with causing death.[55] Research conducted by Victoria University in 2008 confirmed that the natural curiosity of kea which has enabled the species to adapt to its extreme environment, may increase its propensity to poisoning through ingestion of lead – i.e. the more investigative behaviours identified in a bird the higher its blood lead levels were likely to be.[56]
The 1080 pesticide is used to control invasive pest mammals such as stoats and possums and has also been implicated in kea deaths. For example, seven kea were found dead following an aerial possum control operation using 1080, at Fox Glacier in July 2008[57] and a further seven had been found dead in August 2011, following a 1080 aerial possum control operation in Ōkārito Forest.[58] Traps are also considered a risk to kea. In September 2011, hidden cameras caught kea breaking into baited stoat traps in the Matukituki Valley. More than 75% of the traps had been sprung.[59]
Conservation
In the 1970s, the kea received partial protection after a census counted only 5,000 birds. The government agreed to investigate any reports of problem birds and have them removed from the land.[23] In 1986 it was given full protection under the Wildlife Act 1953.Despite being classified as Nationally Endangered in the New Zealand Threat Classification System[60] and endangered in the IUCN Red List and protected by law, kea are still deliberately shot. For example, in the late 1990s, a Fox Glacier resident killed 33 kea in the glacier car park[45] and in 2008, two kea were shot in Arthur's Pass and stapled to a sign.[43] Kea deaths due to traffic have prompted the NZ Transport Agency to install signs to help raise awareness, and to encourage people to slow down if necessary.[61]
A citizen science project called the "Kea Database" was launched in 2017 that allows for the recording of kea observations to an online database. If the recorded kea are banded, it is possible to match up observations with individual named birds, enabling the monitoring of the habits and behaviour of individual kea.[62]
Some are calling for keas to be reintroduced into predator-free zones in the North Island. A former curator of Natural History at Whanganui Regional Museum, Dr Mike Dickison, told North & South magazine in the October 2018 issue that the birds would do well on Mt Ruapehu.[20]
Binomial name
Nestor notabilis
Gould, 1856
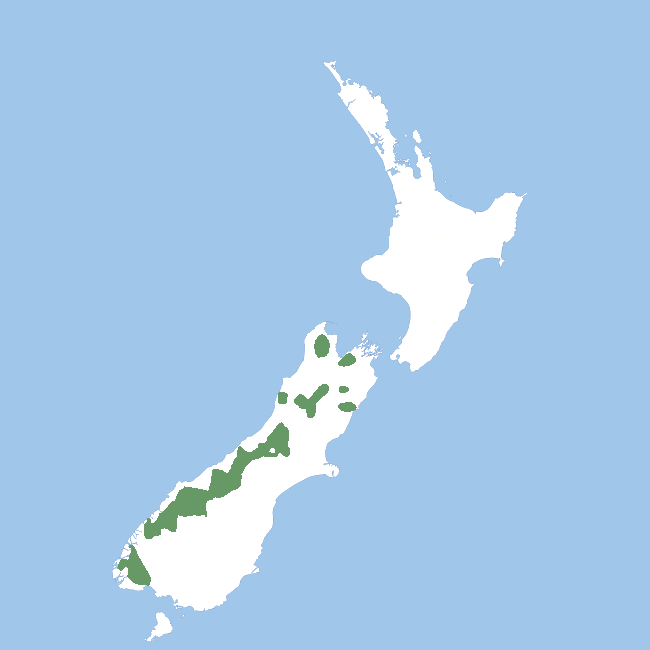
Range in green









No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.