Taxonomy and systematics
Molecular studies have found the hamerkop to be the closest relative of the shoebill.
So far, two fossil relatives of the shoebill have been described: Goliathia from the early Oligocene of Egypt and Paludavis from the Early Miocene of the same country. It has been suggested that the enigmatic African fossil bird Eremopezus was a relative too, but the evidence for that is unconfirmed. All that is known of Eremopezus is that it was a very large, probably flightless bird with a flexible foot, allowing it to handle either vegetation or prey.
Description
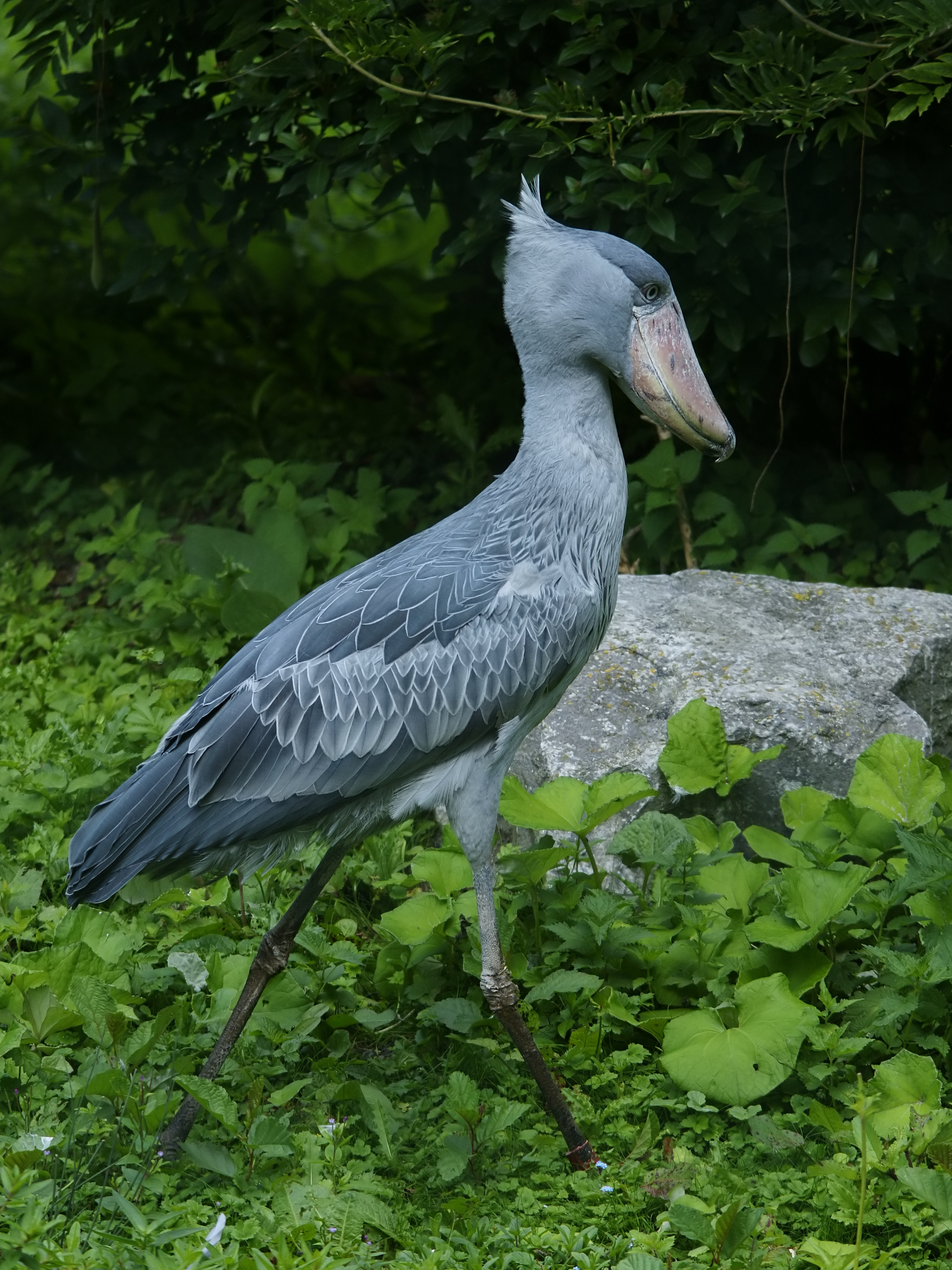
The shoebill's conspicuous bill is its most well-known feature.
The skull
Flight pattern
Its wings are held flat while soaring and, as in the pelicans and the storks of the genus Leptoptilos, the shoebill flies with its neck retracted. Its flapping rate, at an estimated 150 flaps per minute, is one of the slowest of any bird, with the exception of the larger stork species. The pattern is alternating flapping and gliding cycles of approximately seven seconds each, putting its gliding distance somewhere between the larger storks and the Andean condor (Vultur gryphus). When flushed, shoebills usually try to fly no more than 100 to 500 m (330 to 1,640 ft).[9] Long flights of the shoebill are rare, and only a few flights beyond its minimum foraging distance of 20 m (66 ft) have been recorded.Identification
At close range, it can be easily identified by its unique features. In flight, if its unique bill cannot be seen, the shoebill's silhouette resembles that of a stork or condor, but its feathers are a distinctive medium blue-grey. Also unusual, its tail is the same colour as its wings. Under poor viewing conditions, its size and wingspan can distinguish it from other birds in its habitat. Its legs, roughly the length of storks', extend straight back far past its tail when in flight. The wing to tail size cannot be used for identification; it is similar to those of several other birds.
A shoebill at a zoo, (video)
Distribution and habitat
The shoebill is distributed in freshwater swamps of central tropical Africa, from southern Sudan through parts of eastern Congo, Rwanda, Uganda, western Tanzania and northern Zambia. The species is most numerous in the West Nile sub-region and adjacent areas of the south Sudan; it is also significant in wetlands of Uganda and western Tanzania. More isolated records have been reported of shoebills in Kenya, the Central African Republic, northern Cameroon, south-western Ethiopia, Malawi. Vagrant strays to the Okavango Basin, Botswana and the upper Congo River have also been sighted. The distribution of this species seems to largely coincide with that of papyrus and lungfish. The shoebill is non-migratory with limited seasonal movements due to habitat changes, food availability and disturbance by humans.[9]The shoebill occurs in extensive, dense freshwater marshes. Almost all wetlands that attract the species have undisturbed Cyperus papyrus and reed beds of Phragmites and Typha. Although their distribution largely seems to correspond with the distribution of papyrus in central Africa, the species seems to avoid pure papyrus swamps and is often attracted to areas with mixed vegetation. More rarely, the species has been seen foraging in rice fields and flooded plantations.[9]
Behaviour and ecology
The shoebill is noted for its slow movements and tendency to stay still for long periods, resulting in descriptions of the species as "statue-like". They are quite sensitive to human disturbance and may abandon their nests if flushed by humans. However, while foraging, if dense vegetation stands between it and humans, this wader can be fairly tame. The shoebill is attracted to poorly oxygenated waters where fish frequently surface to breathe. Exceptionally for a bird this large, the shoebill often stands and perches on floating vegetation, making them appear somewhat like a giant jacana, although the similarly-sized and occasionally sympatric Goliath heron (Ardea goliath) is also known to stand on aquatic vegetation. Shoebills typically feed in muddy waters and, being solitary, forage at 20 m (66 ft) or more from one another even where relatively densely populated. This species stalks its prey patiently, in a slow and lurking fashion. While hunting, the shoebill strides very slowly and is frequently motionless. Unlike some other large waders, this species hunts entirely using vision and is not known to engage in tactile hunting. When prey is spotted, it launches a quick violent strike. However, depending on the size of the prey, handling time after the strike can exceed 10 minutes. Around 60% of strikes yield prey. Frequently water and vegetation is snatched up during the strike and is spilled out from the edges of the mandibles. The activity of hippopotamus may inadvertently benefit the shoebill, as submerged hippos occasionally force fish to the surface.[9]Shoebills are largely piscivorous but are assured predators of a considerable range of wetland vertebrates. Preferred prey species have reportedly included marbled lungfish (Protopterus aethiopicus) and Senegal bichir (Polypterus senegalus) and various Tilapia species and catfish, the latter mainly in the genus Clarias. Other prey eaten by this species has included frogs, water snakes, Nile monitors (Varanus niloticus) and baby crocodiles. More rarely, turtles, snails, rodents and small waterfowl have reportedly been eaten. There is a single report of shoebills feeding on lechwe (Kobus leche) calves, but this would need confirmation. Given its sharp-edged beak, huge bill and wide gape, the shoebill can hunt large prey, often targeting prey bigger than is taken by other large wading birds. Fish eaten by this species are commonly in the range of 15 to 50 cm (5.9 to 19.7 in) long and weigh around 500 g (1.1 lb), though lungfish of as much as 1 m (3.3 ft) have been attacked. Snakes preyed upon are commonly from 50 to 60 cm (20 to 24 in) long. In the Bangweulu Swamps of Zambia, the main prey items fed to young by the parents were the catfish Clarias gariepinus [10](syn. C. mossambicus) and water snakes. In Uganda, lungfish and catfish were mainly fed to the young.[9] The big beak is sometimes used to dig into pond-bottom mud to extract lungfish from their aestivation burrows.
Breeding
A shoebill sitting on the nest in Prague Zoo
Voice
The shoebill is normally silent, but they perform bill-clattering displays at the nest.[2] When engaging in these displays, adult birds have also been noted to utter a cow-like moo as well as high-pitched whines. Both nestlings and adults engage in bill-clattering during the nesting season as a means of communication. When young are begging for food, they call out with a sound uncannily like human hiccups. In one case, a flying adult bird was heard uttering hoarse croaks, apparently as a sign of aggression at a nearby marabou stork (Leptoptilos crumeniferus).[9]Status and conservation
The population is estimated at between 5,000 and 8,000 individuals, the majority of which live in swamps in Sudan, Uganda, eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Zambia.[11] There is also a viable population in the Malagarasi wetlands in Tanzania.[12] BirdLife International has classified it as Vulnerable with the main threats being habitat destruction, disturbance and hunting.Relationship to humans
This species is considered to be one of the five most desirable birds in Africa by ornithologists.[13] There are Egyptian images depicting the shoebill, while the Arabs referred to the bird as abu markub, which means one with a shoe, a reference to the bird's distinctive bill.[citation needed]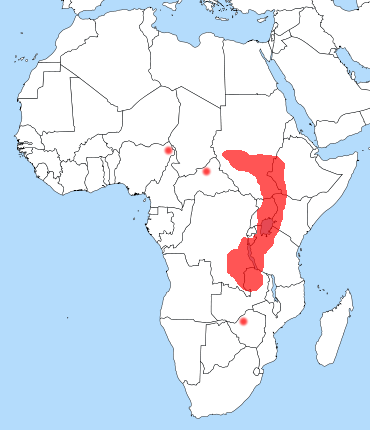







No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.